![]()
Data Quality & Profiling
Improve data quality and increase trust in your data with data profiling, lineage & more.![]()
Dataedo AI
Create auto object descriptions and get help from AI chat in finding tables & writing queries. Business Glossary Build and share a universal glossary of business terms, policies and rules.![]()
Data Classification
Find and tag sensitive data in your databases to comply with data protection regulation.![]()
Data Community
![]()
Domains
![]()
Reference Data Management
![]()
StewardHub
![]()
Schema Change Tracking
![]()
Workflows

SQL Server
Power Bi
Tableau

Qlik Sense soon

Databricks
Microsoft Fabric
Azure
AWS

Oracle
![]()
Metadata Scanning
![]()
Product Tour
![]()
Why Dataedo
Book a demo Try Dataedo
Data dictionary is an inventory of data elements in a database or data model with detailed description of its format, relationships, meaning, source and usage.
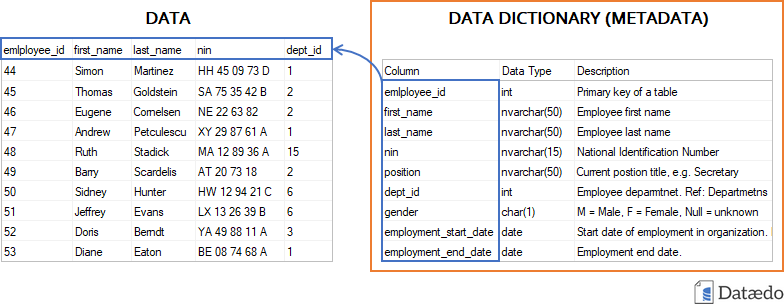
You can classify data dictionary into two main categories:
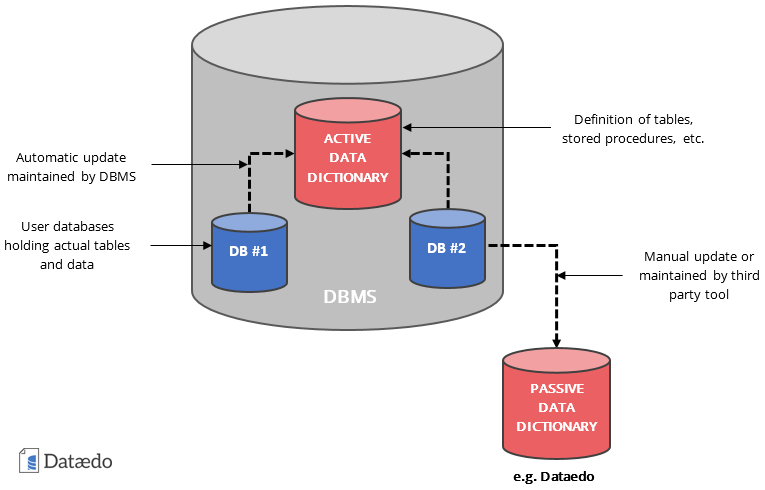
Active data dictionary is built into majority of database management systems (DMBS). It is accessible to users with a set of system tables or views and present information about tables, columns, data types, scripts and other objects in the database.
Every database schema update (using DDL scripts, such as ALTER TABLE) is automatically reflected in active data dictionary, so it does not require any maintenance from the database admin.
System Catalog, System Tables, Data Dictionary Views, Catalog Views. it has many names. System Catalog is a set of system tables or views built into a database engine (DBMS) to allow user to access database metadata - information about tables, columns, scripts, and other database objects. It also includes information about security, logs or health.
Information Schema is a standard System Catalog defined by SQL-92. It is an dedicated schema named information_schema with a set of predefined system views or tables. Even though it being a standard, every vendor implemented this standard to certain extend and added its own tables and columns.
Some of the tables in information_schema:
Sample Information Schema query:
select * from information_schema.tables Here is a compilation of system catalogs (data dictionaries) in different database engines:
| Database | Catalog | Schema | Prefix |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon Redshift | System Catalog Tables | pg_* | |
| Amazon Redshift | SVV views | svv_* | |
| Azure SQL Database | System Catalog Views | sys | |
| Azure SQL Database | Information Schema | information_schema | |
| Firebird | System Tables | RDB$ | |
| IBM Db2 | Catalog views | SYSCAT | |
| IBM Informix | System Catalog Table | informix | sys* |
| IBM Informix | Information Schema | information_schema | |
| Interbase | System Tables | RDB$ | |
| MariaDB | Information Schema | information_schema | |
| Microsoft Access | Database object listing (MSysObjects) | ||
| MySQL | Information Schema | information_schema | |
| Oracle | Data Dictionary Views / Catalog Views | SYS | ALL_, USER_, DBA_ |
| PostgreSQL | System Catalogs | pg_* | |
| SAP HANA | System Views | sys | |
| SAP/Sybase ASE | System Tables | sys* | |
| Snowflake | Information Schema | information_schema | |
| SQL Server | System Catalog Views | sys | |
| SQL Server | Information Schema | information_schema | |
| SQLite | System Table | sqlite_master | |
| Teradata | Data Dictionary Views | DBC | |
| Vertica | System Tables | v_catalog |
Passive data dictionary is separate from the database and all changes in database structure need to be applied in the passive data dictionary manually, or with dedicated software.
Passive data dictionary can take different forms:
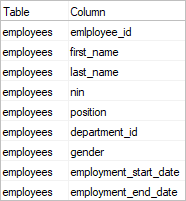
Data dictionary is a table with data elements (columns) as rows and their attributes as columns. Specific attributes vary depending on the purpose of the data dictionary.
Data dictionary has 2 essential elements:
Minimum data dictionary:
Relational database engines enable much more description of data models and provide this information through their data dictionaries. This information is:
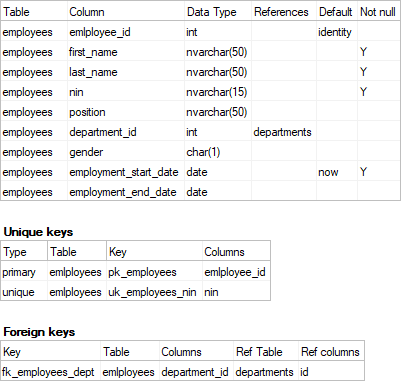
There are more attributes for each table or column that architects, teams or organizations might want to collect that are not supported by database engines. It all depends on the purpose of the data dictionary. Those attributes could be:
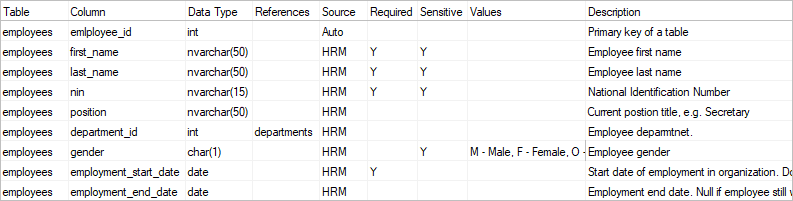
In such case teams can collect this information in external document or dedicated software (referred to as data dictionary tool, metadata repository, data catalog).
Data dictionary can be used for different purposes. Those key purposes are:
All major relational database management systems store information about data structures in a special structures – predefined tables or views that hold metadata about each element of a database – tables, columns, indexes, foreign keys, constraints and so on.
This type of data dictionary serves the purpose of providing information to users and tools about the database schema - all elements of data model and programs.
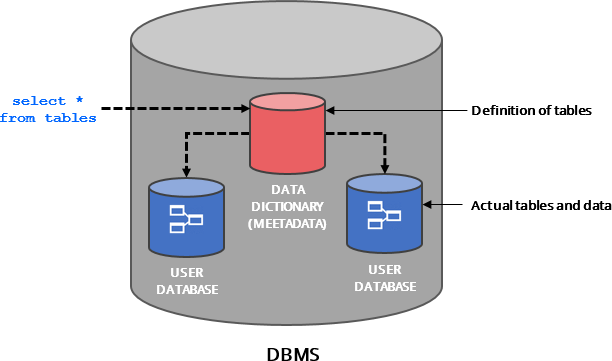
Learn more:
Data Dictionary can be used as a tool to model data. This can be done with dedicated data modeling tool or plain spreadsheet or document. In this case data dictionary serves as a specification of entities and their fields and helps business analysts, subject matter experts and architects to gather requirements and model the domain. Physical database and application is then designed and implemented based on this document.
Data dictionary can also be used as a reference and cataloging of existing data assets - tables in databases, spreadsheets, files and so on.
This can be achieved with a few formats and tools:
Data Dictionaries exist in a few different forms:
Most common occurrence of data dictionary is the one built into most database systems, often referred to as data dictionary, system catalog or system tables.
Data Dictionary can be in a form a text or HTML document or spreadsheet, detached form any physical data source. We can further split this form into:
Organizations that are mature in their data governance implement special software that extracts, manages and provides access to data dictionary of data assets in multiple databases. This software can be called Metadata Repository (broader term) or Data Catalog (more specific and trending concept).
Diagram below shows where data dictionary appears in the process of design, management and documentation of databases.